As the world of design, fabrication, and manufacturing continues to evolve, 2D and 3D visualization has become a powerful platform of attraction. Within the building and construction industry, the shift from traditional drafting to advanced 3D modelling workflows is happening at a rapid pace. While 2D drawings still play an important role, 3D models offer greater efficiency, accuracy, and realistic visualization, making it easier to understand designs, reduce errors, and bring ideas to life in ways that 2D methods often struggle to achieve.
Even as the future leads us toward a fully digital 3d driven workflow, issuing 2d drawings often in paper remains an essential part of the process.
In current reality, Despite the increasing influence of 3d modelling capabilities and the promise of fully integrated 3d model 2d drawing continues to influence the construction and manufacturing industry.
Today as the landscape of data visualization moves on in a rapid way the process chosen to present information may significantly influence comprehension and decision making.
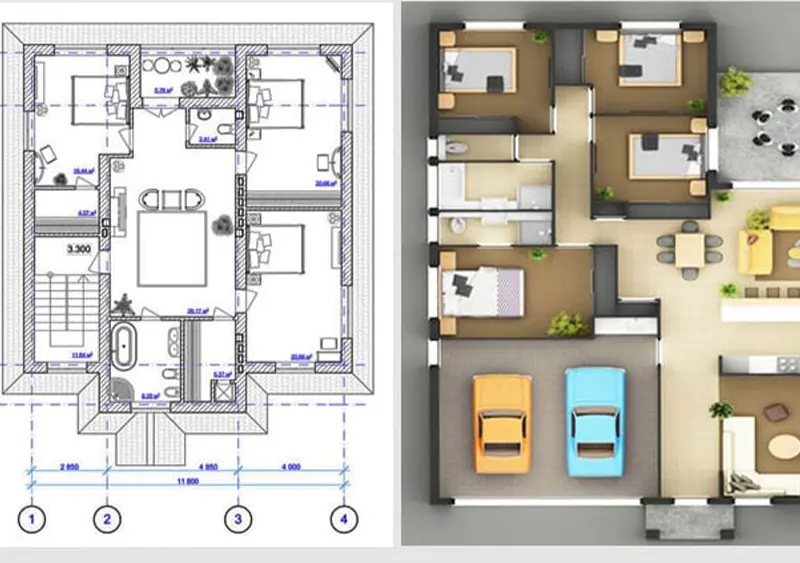
Two Widely Used Techniques Are 2D And 3D Visualization.
Each has its own strength and weakness but 3d visualization often stands out for its ability to offer a more immersive and detailed representation of data .
2d visualization is the traditional method of representing data employing flat two dimensional images such as chart graphs and maps.
Pros :
1. Simplicity –
The greatest strength of 2d visualization lies in its simplicity.
Tools like bar graphs, pie charts and line graphs are straightforward and may be interpreted by a broad audience.
This simplicity makes 2d visualization ideal for quick high overviews of data.
2. Accessibility –
Because 2d visualization is familiar to most people they are very much universally available and they do not require specialized knowledge to be proficient in it.
This makes them effective for communication in various settings from board room presentation to educational classroom.
3. Performance –
2d visualization generally less computational power which means they might be rendered quickly and easily on most device
This efficiency is particularly beneficial while working with large data sets or in an environment where there is technology like the computer.
4. Cost effective –
Creating 2d visuals is typically less expensive and time consuming compared to 3d visuals.
Tools for generating 2d charts and graphs are often quickly available and user friendly thus reducing the need for specialized skill or expensive software.
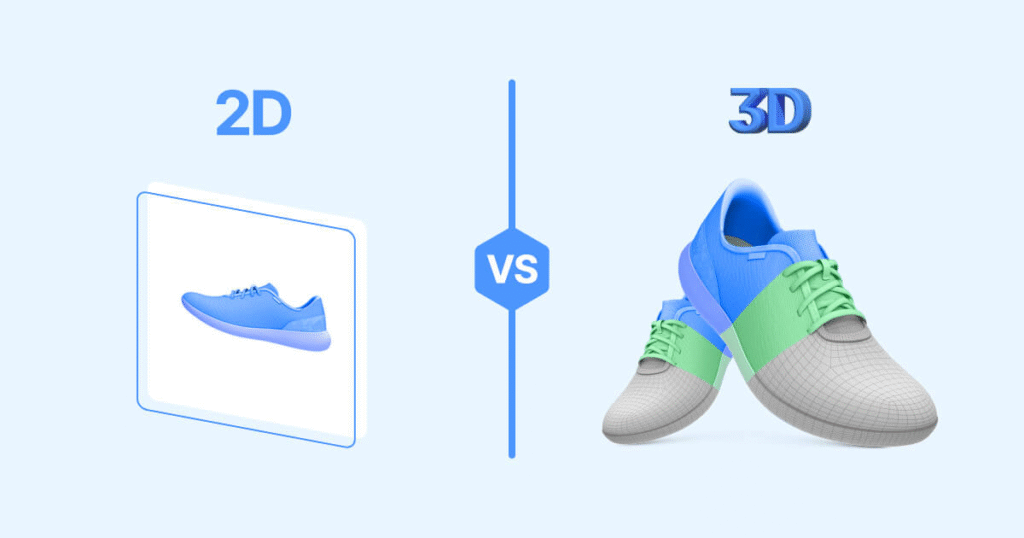

Cons :
1. Limited Depth –
The primary drawback of 2d visualization is its inability to represent complex data sets with depth.
For data that involves various variables or intricate relationships, 2d visualization may over simplify and fall to capture the full picture.
2. Engagement –
2d visuals may not be as engaging or immersive as 3d visuals .
This may be a remarkable disadvantage in fields where capturing the viewers attention is crucial, such as marketing, education or interactive presentation.
3. Context –
Without the ability to manipulate the view, 2d visuals often miss out on providing a comprehensive context specially for spatial or geospatial data.
Users are limited to fixed perspectives which might obscure important sights.
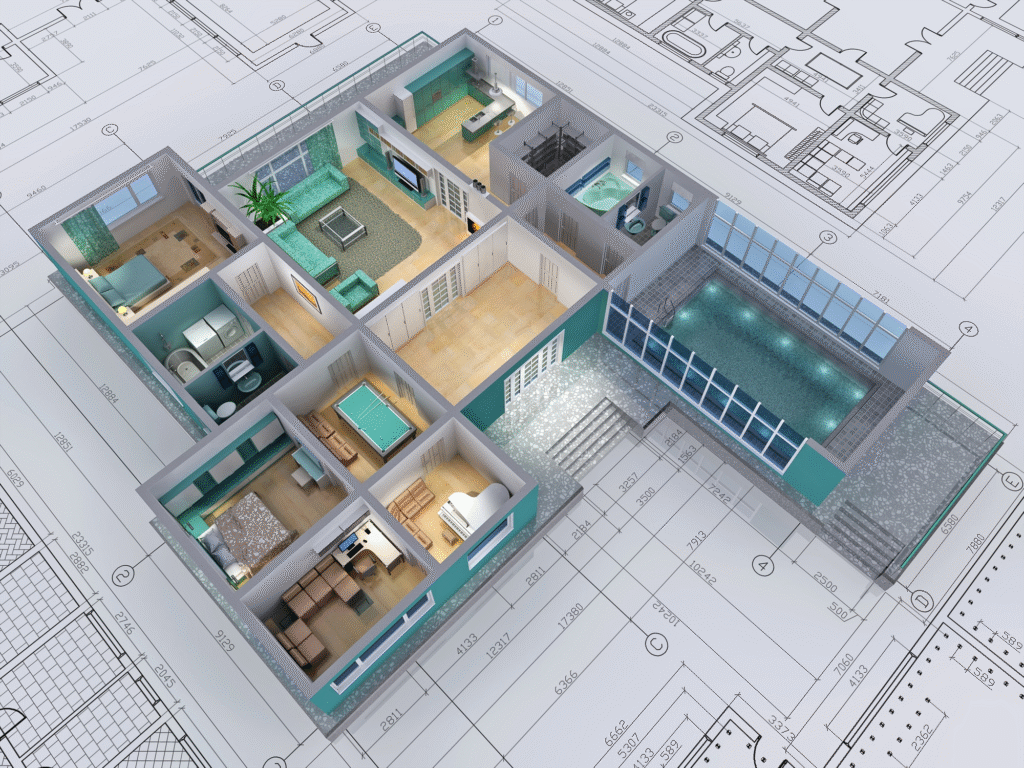
4. 3d Visualization –
3d visualization on the other hand employs three dimensional models to represent data , offering a more dynamic and immersive experience.
5. Depth And Detail –
3d visualization offers a richer representation of data showcasing depth and additional dimension that 2d visuals cannot.
This is particularly useful in fields like medicine engineering and environment science where understanding spatial relationships is critical.
6. Interactivity –
One of the standout features of 3d visualization is its interactivity.
Users may manipulate 3d models by rotating, zooming and exploring enhances their understanding and engagement with data .
This interactive capability is invaluable for training simulation and exploratory data analysis.
7. Realism –
3D visuals may provide a more realistic and immersive experience .
For instance architects and urban planners use a 3d model to create lifelike representation of buildings and cities enabling stakeholders to visualize projects before they are built.
8. Complex data representation –
3d visualization excels at representing complex data sets spatial information in scientific research for instance 3d models may illustrate intricate biological structure or geological formation in ways 2d representation.
2D and 3D Visualization: Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Communication
2D and 3D visualization are powerful tools used to present information clearly and meaningfully. 2D visualization focuses on simplicity and speed, making it well suited for charts, diagrams, and reports where data needs to be understood quickly without distraction.
In contrast, 3D visualization allows information to be explored with depth and spatial accuracy. It helps users better grasp complex structures and relationships, which is especially useful in industries such as architecture, engineering, medical imaging, and geospatial analysis.
As technology evolves, 3D visualization tools are becoming easier to use and more affordable, increasing their adoption across different sectors. At the same time, 2D visualization continues to remain essential because clear and straightforward visuals often communicate ideas more effectively.
The choice between 2D and 3D visualization depends on the type of data, the message being conveyed, and the audience. When applied correctly, both methods complement each other to enhance understanding and communication.

Join MAAC Kolkata Today & Make An Awesome Career in 2D And 3D Industry.
Ph. No. – 8981005311 MAAC CHOWRINGHEE
Ph. No. – 8981006211 MAAC RASHBEHARI
Ph. No. – 8981009211 MAAC ULTADANGA




